What you need to know about REIT
REIT stands for Real Estate Investment Trust. It is a type of investment vehicle that pools together funds from multiple investors to invest in real estate assets such as properties, mortgages, or other real estate-related investments.
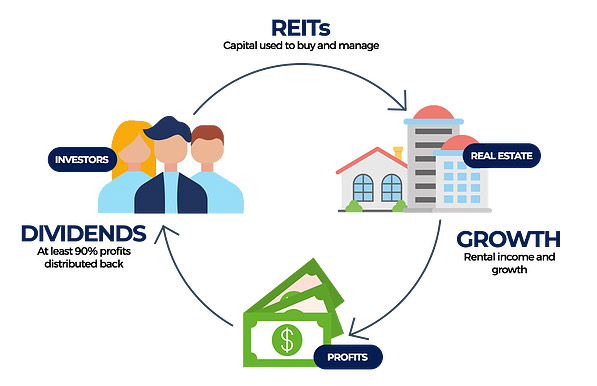
REITs provide individual investors with an opportunity to invest in large-scale, income-producing real estate. They are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, which makes them an attractive investment option for those seeking regular income.
REITs can be publicly traded on stock exchanges, allowing investors to easily buy and sell shares, or they can be privately held. Publicly traded REITs are subject to the same regulatory requirements as other publicly traded companies, including regular financial reporting and disclosure requirements.
There are several types of REITs, each with its own investment focus and strategy. Some of the most common types include:
Equity REITs: These are the most common type of REITs that own and operate income-producing real estate properties such as apartments, shopping centers, office buildings, industrial parks, and hotels. Equity REITs generate revenue from rent paid by tenants and appreciation in the value of their properties.
Mortgage REITs: Also known as mREITs, these REITs invest in real estate mortgages instead of physical properties. They generate revenue by earning interest on the mortgages they hold or by buying and selling mortgage-backed securities.
Hybrid REITs: These REITs invest in both physical properties and real estate mortgages. They combine the income-generating potential of equity REITs with the interest income potential of mortgage REITs.
Public Non-Listed REITs: These are REITs that are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) but are not listed on a stock exchange. They are usually sold through financial advisors or brokers and can offer investors access to a diversified portfolio of properties.
Private REITs: These are not publicly traded and are not registered with the SEC. They are typically only available to high-net-worth investors and institutions and can offer higher returns but with higher risks and less liquidity.
Sector-specific REITs: These REITs invest in specific types of real estate, such as healthcare facilities, data centers, storage facilities, or timberlands.
Investors should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance when choosing which type of REIT to invest in.
Evana Valenzuela, AB life investor



